Nowadays, there are countless plant extracts added to skincare products, and it’s hard to tell how effective and stable the ingredients are. Today, we are going to talk about the application of olive leaf extract in skincare products.
Olives can be used for oil, and medicine and polished into strings, and olive oil is mainly extracted from the fruit. What we are going to talk about today, however, is the extracted components of olive leaves. There are five main groups of phenolic compounds in olive leaves: oleuropein, flavonoids, flavonols, flavonols, and phenolic substitutes.
Oleuropein, the most biologically active of them all, is the main component of the polyphenolic cleaved-one ether terpenes in olive leaves.
Oleuropein is distributed throughout the olive tree, but the content varies from one part to another, with the highest content in the leaves. Therefore, for the extraction of Oleuropein from olive leaves, several ways have been explored industrially and a well-established pattern has been developed.
There is a large body of literature, which suggests that Oleuropein and its derivatives have a variety of biochemical effects, including anti-inflammatory effects, anti-thrombotic, prevention of LDL oxidation and platelet aggregation, anti-ischemic, antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects.
Oleuropein, which also has strong antioxidant activity in vitro, derives its strong antioxidant activity from its adventitious dihydroxy-substituted structure, which means that it can bind superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide radicals, and nitro radicals to scavenge free radicals. Free radicals are an important component of the ‘oxidation’ reaction, and scavenging free radicals is an important ‘antioxidant’ action.
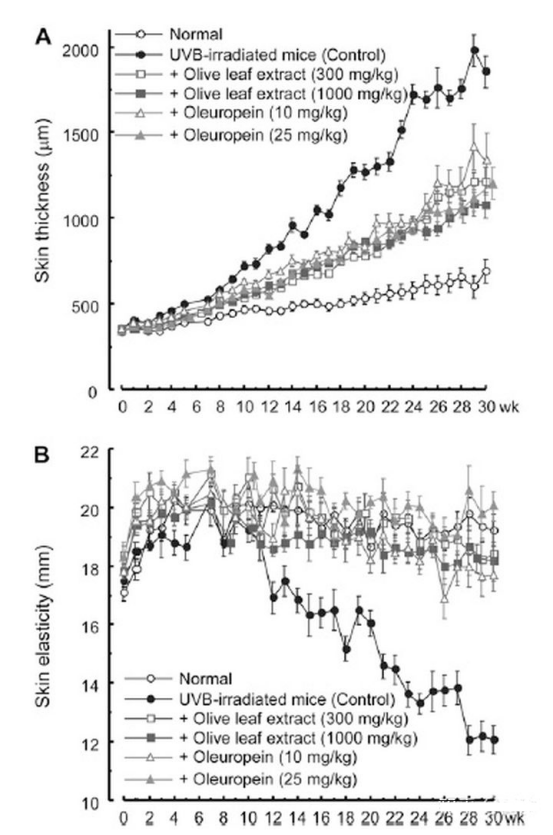
This is an experiment by Japanese scientists who irradiated the backs of hairless mice with UV light and recorded the thickness (epidermis + dermis) and elasticity of the skin. Generally, the skin after UV light irradiation will show thickened thickness but decreased elasticity and increased brittleness, which is a sign of skin photoaging.
The experiment was divided into 6 groups: normal skin, UV-irradiated skin, UV-irradiation + olive leaf extract 300mg/kg, UV-irradiation + olive leaf extract 1000mg/kg, UV-irradiation + olive bitters 10mg/kg, and UV-irradiation + olive bitters 25mg/kg, and their skin thickness and elasticity were measured at even weeks, respectively, and The graphs were prepared as above.
We found that the skin of normal mice thickened with age and the elasticity was relatively stable, while the skin of UV-irradiated mice thickened rapidly and was about 4 times thicker than that of the non-UV-irradiated group by 30 weeks of age, and the elasticity decreased significantly to about 2/3 of the original level.
However, in mice treated with olive leaf extract, skin thickness was controlled to be twice that of the non-UV irradiated group, with only a small decrease in elasticity.
The article concluded that Oleuropein is the main active component of olive leaf extract and has good photoprotective and antioxidant effects.
In terms of anti-inflammatory and anti-infection, in 1970, Juven et. reported that ethyl acetate extract of the olive leaf had good antibacterial activity, which was isolated and identified mainly as Oleuropein and glycosides, and Oleuropein could inhibit the growth of Bradyrhizobium, Rhizoctonia and Rhynchococcus, and in 1999, Bisignano et. reported that it could inhibit Haemophilus influenza, Salmonella and Staphylococcus aureus, and some reports suggest that its inhibitory effect may be to damage the cell wall of bacteria to make them lose protection and penetrate their cell membrane leading to cell membrane damage and prandial, but the mechanism of inhibition varies from bacteria to bacteria and needs further study.
In a trauma model test on mice [9], it was confirmed that on the 3rd and 7th day after trauma, mice in the group with Oleuropein had more skin VEGF and type I collagen synthesis and faster skin healing in comparison with mice without it.
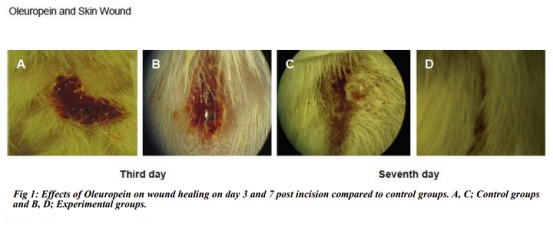
(A, C: control group without Oleuropein, B, D: experimental group with Oleuropein)
In conclusion, the main active ingredient of olive leaf extract is Oleuropein, which has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-bacterial effects, and can be used as a moisturizing repair during the recovery period of certain skin problems, for sensitive skin, or for daily maintenance.