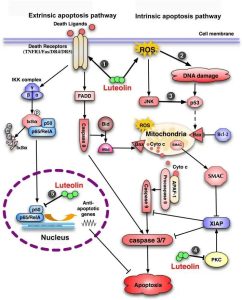
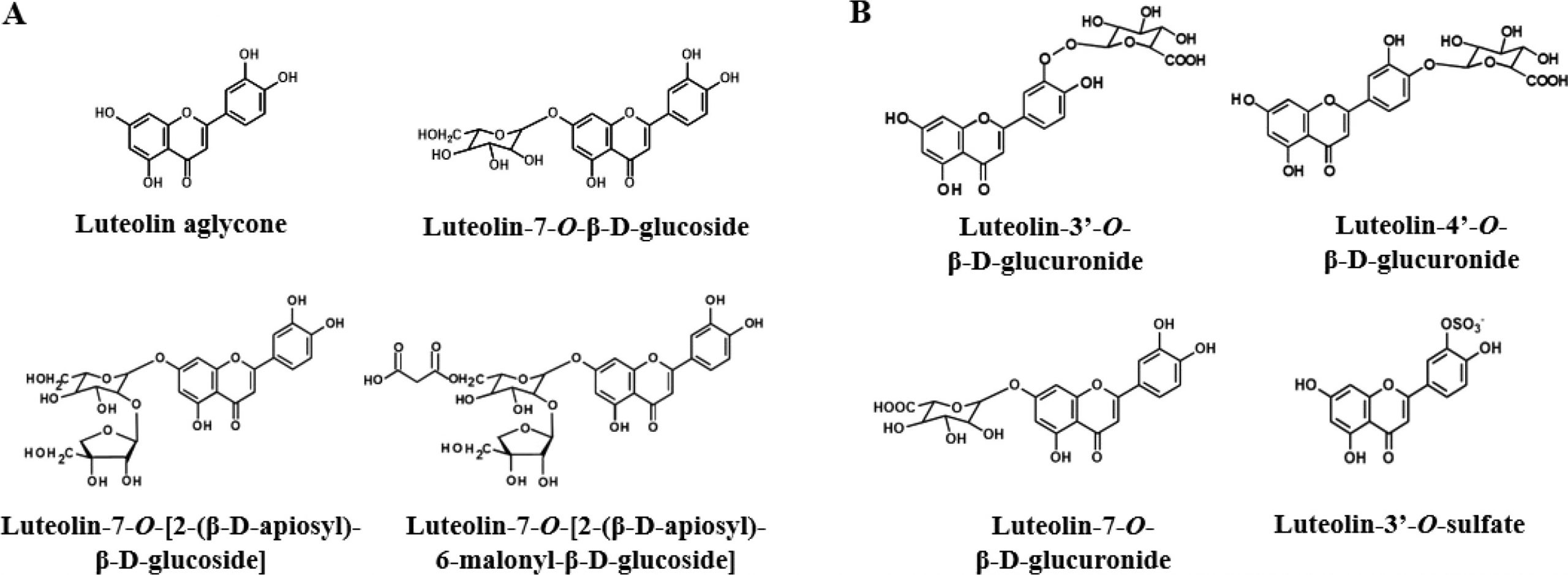
Luteolin is a plant-derived flavonoid that exists in a variety of traditional Chinese medicines and has a wide range of pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, uric acid-lowering, anti-tumor, anti-bacterial, and anti-viral, etc.
It is mainly used clinically for cough suppression, expectorant, anti-inflammatory, uric acid-lowering and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Recently, Liu Bin and Zhao Chao from the School of Food Science, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, China, discovered that 6, 8 -guanidine lignocaine quinone-chromium complex (GLQ.Cr), a derivative of luteolin, could improve blood glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice by regulating hepatic PPAR signaling pathway and modulating gut microbial composition, which brings new hope for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes.
1. The role of Luteolin
Luteolin, mostly in the form of glycosides, exists in a variety of plants, including whole-leaf cymbidium, pepper, wild chrysanthemum, honeysuckle, and perilla. Studies have shown that Luteolin inhibits macrophage phosphorylation, inhibits the activity of transcription factor NF-kB, and is able to inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of cytokines IL-6 and TNF-a by macrophages. lignans also increase IFN-γ, decrease specific Ig-E, and reduce eosinophil infiltration. According to Professor Hu Renming’s theory of metabolic inflammatory syndrome, metabolic inflammatory diseases such as type 2 diabetes are due to macrophage polarisation related. Therefore, there is a theoretical basis for Lueolin to improve type 2 diabetes.

2. Luteolin derivatives improve blood glucose in mice
The team of Liu Bin and Zhao Chao from the School of Food Science, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University used Lueolin as a lead compound to synthesize 6, 8 -guanidine Lueolin-chromium complex (GLQ.Cr) using free radical reaction, C-N cross-coupling reaction and ligand reaction and then observed its effects on mice with type 2 diabetes.
(1). GLQ.Cr alleviated the symptoms of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice by improving liver and pancreatic function and regulating the intestinal microbiota.
(2). GLQ.Cr regulates abnormal glucose metabolism mainly by affecting the hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway.
(3). GLQ.Cr was found to improve blood glucose levels, pancreatic islet function, and tissue inflammatory response in type 2 diabetic mice by modulating intestinal flora structure and increasing short-chain fatty acid content through fecal transplantation.